How The Water Shapes Us
A photo essay of the people and places within the Mississippi River basin
The Mississippi River flows straight through the heart of America. The river and its tributaries have carved the land, shaped ecosystems, built economies and influenced cultures in thirty one states across the country. Nature Conservancy magazine asked photographers within ten of those states to document how water influences life throughout this rich and varied river system.
_________

Photographs by: Ackerman + Gruber
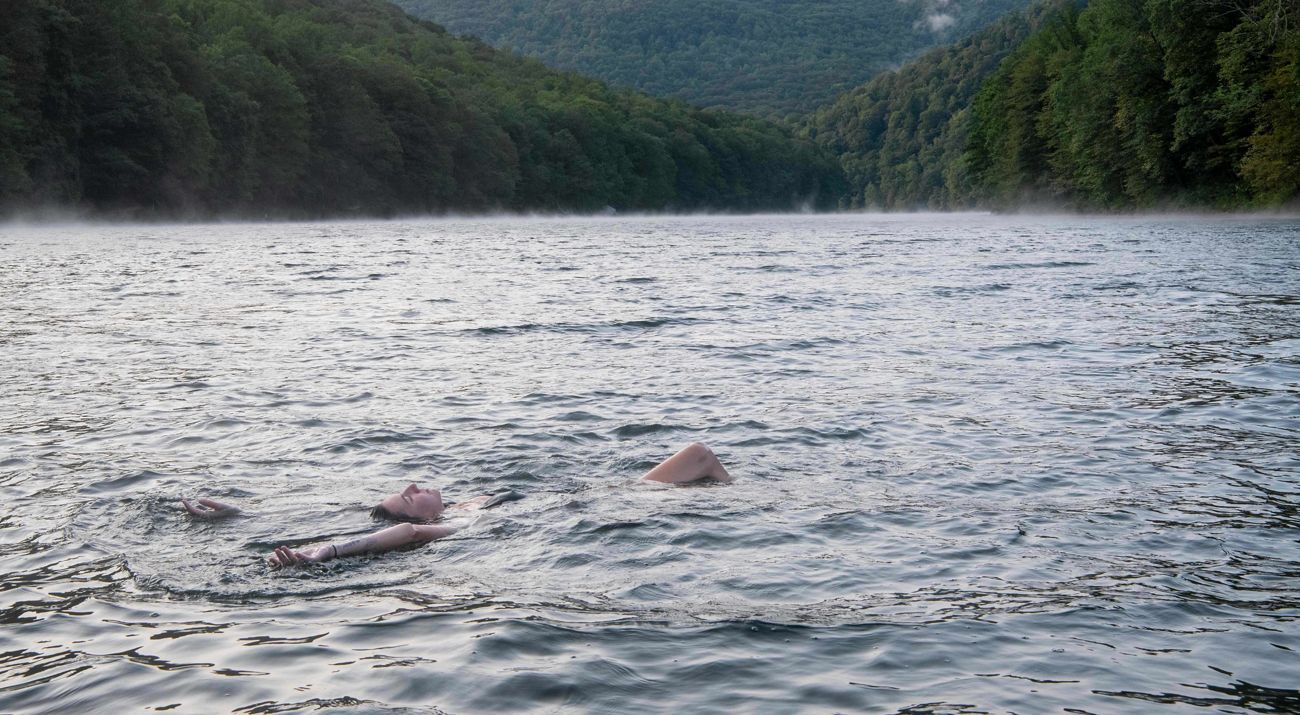
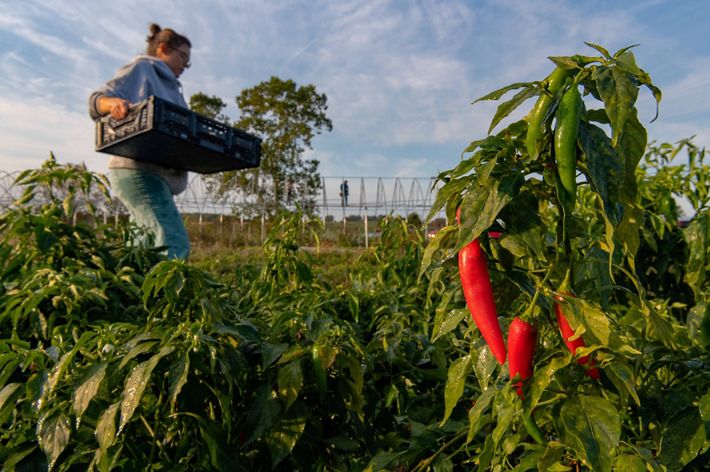
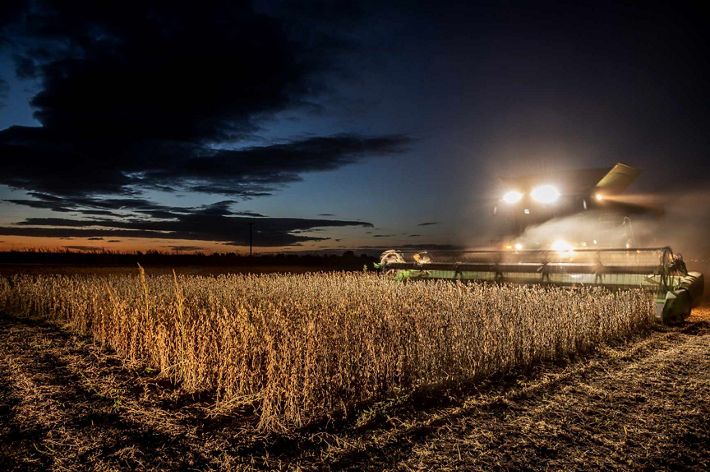
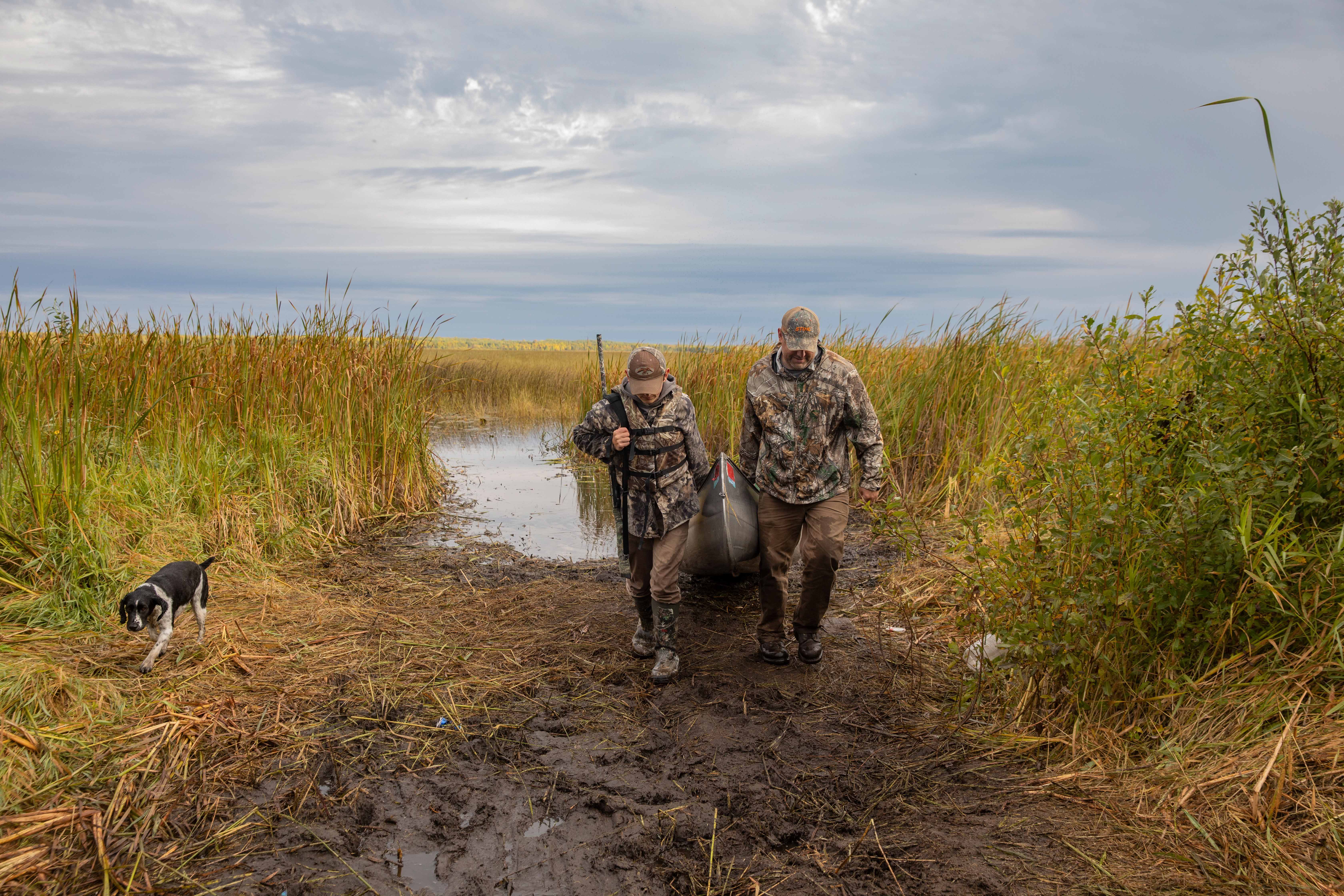
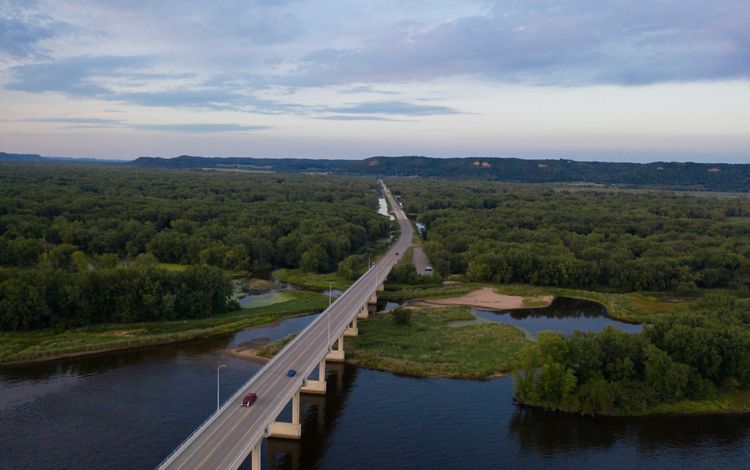
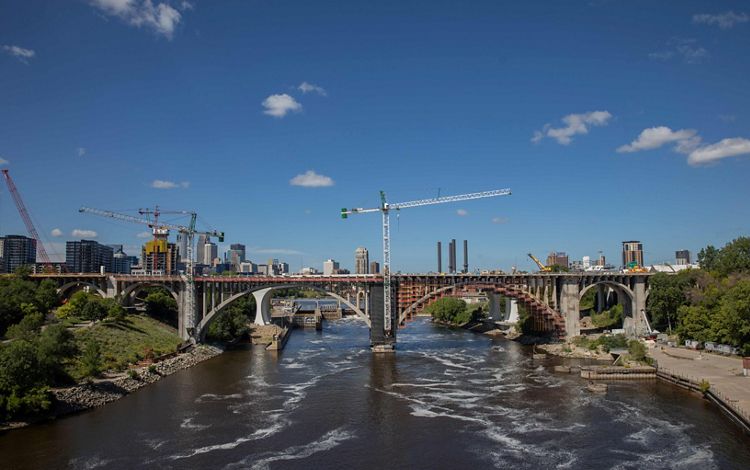
MINNESOTA
Our photo coverage begins at the beginning: the Mississippi River headwaters in northern Minnesota. The river starts at Lake Itasca and forms an 18-foot-wide ribbon of water that flows through state parks, small towns and Minneapolis/St. Paul before winding its way to the border Minnesota shares with Wisconsin. Cabins are studded along the shores of lakes and within forests near the headwaters. About one quarter of Minnesota drains into that waterway—a source of clean drinking water and rich biodiversity and an economic driver for the state’s residents. Many recreational activities such as camping, hiking, hunting, and fishing occur here as well as agricultural practices such as wild rice harvesting.
Find out more about how TNC is protecting this vital region here.
Minnesota



_________

Photographs by: Louise Johns
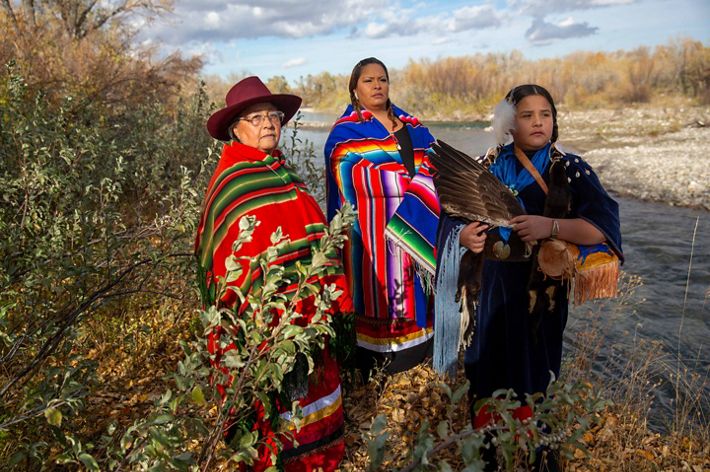
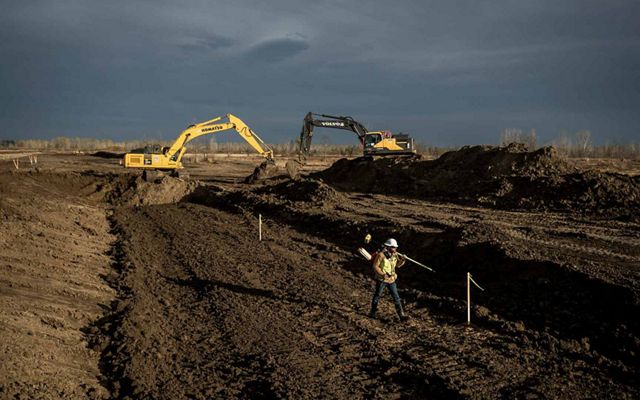
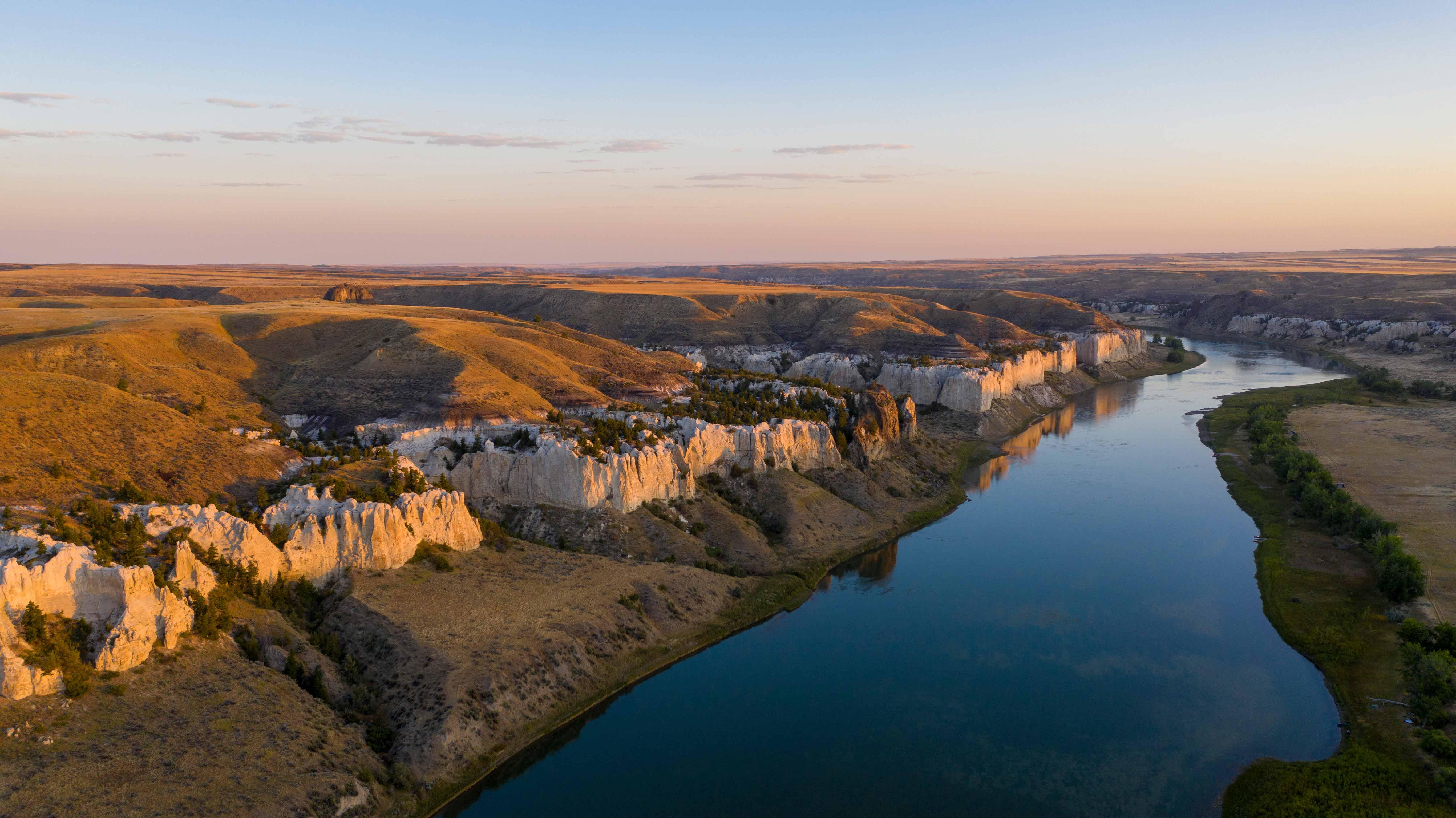
MONTANA
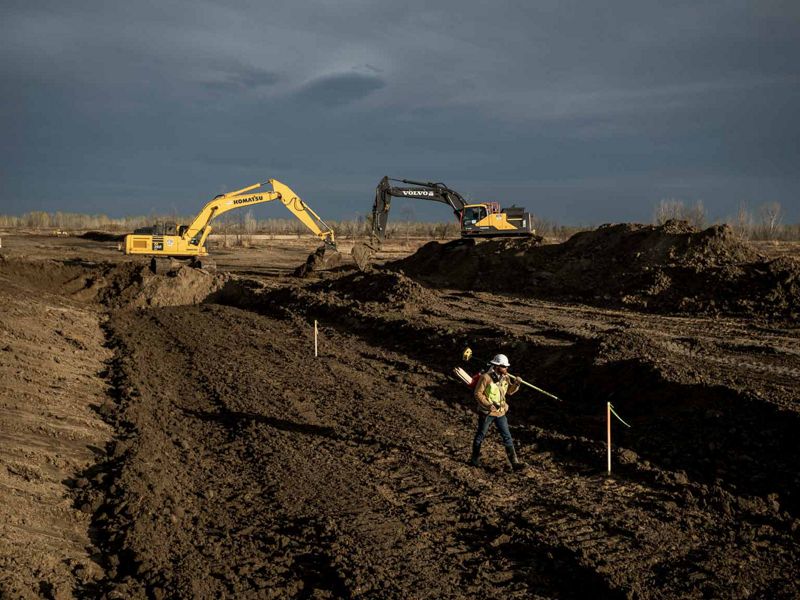
The westernmost reaches of the Mississippi River basin extend into Montana, where we find the Yellowstone and Missouri River tributaries. These waterways pass through dramatic landscapes that include mountains, prairies and rock formations such as the Upper Missouri River Breaks National Monument. Water is in high demand in the west and Montana is no exception. The Missouri River has suffered from historically low water levels in recent years due to lower-than-average rain and snowfall in the region. It’s something that residents are keeping an eye on, especially farmers and ranchers in the region. Click here for more information about how TNC in Montana is working to protect freshwater throughout this state.
MONTANA
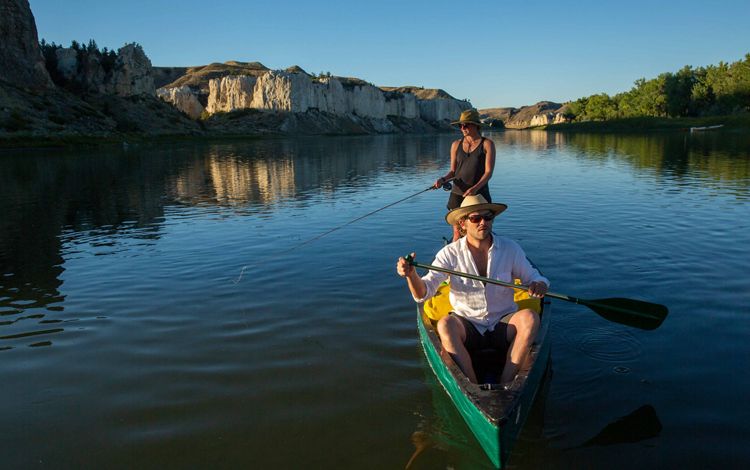
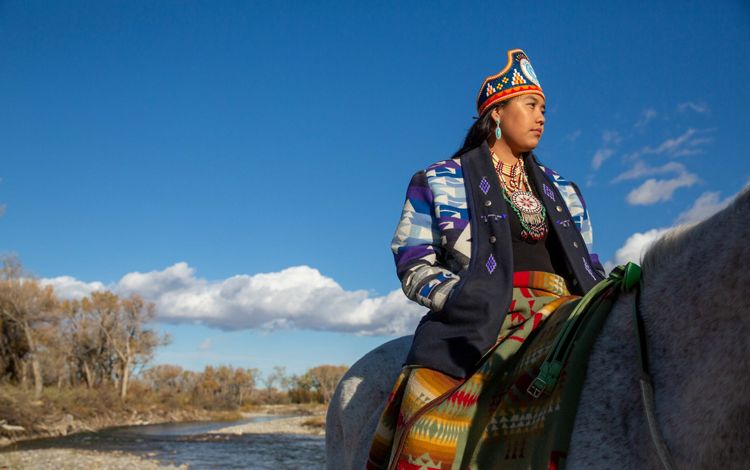
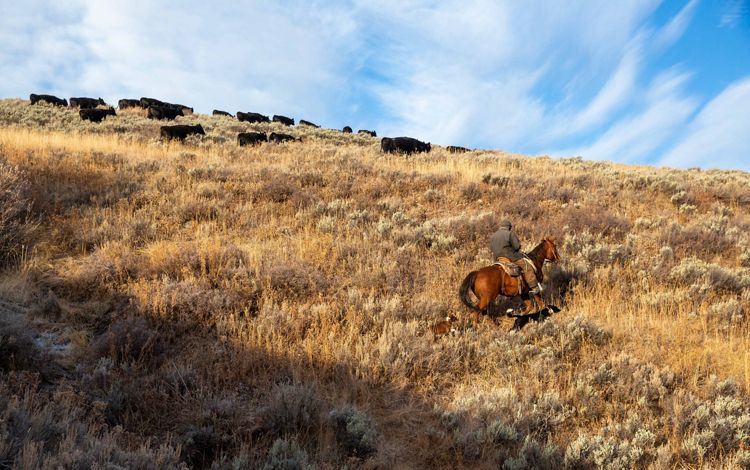
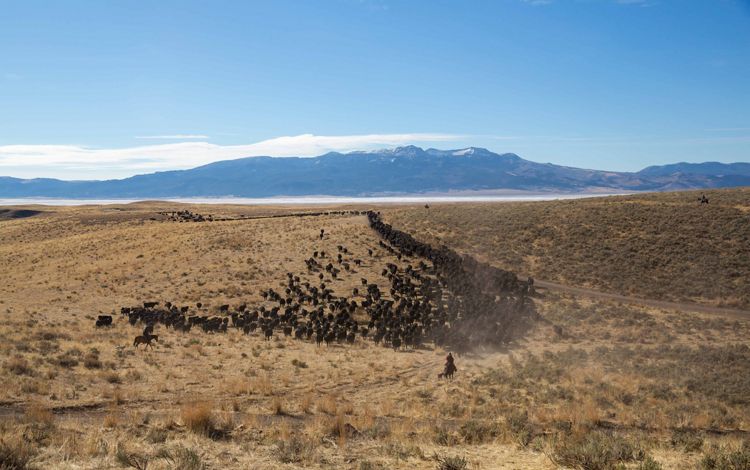




_________

Photographs by: Raymond Thompson Jr.
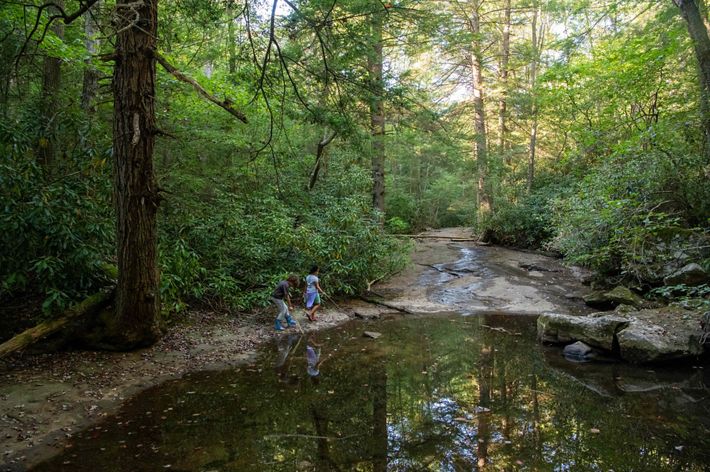
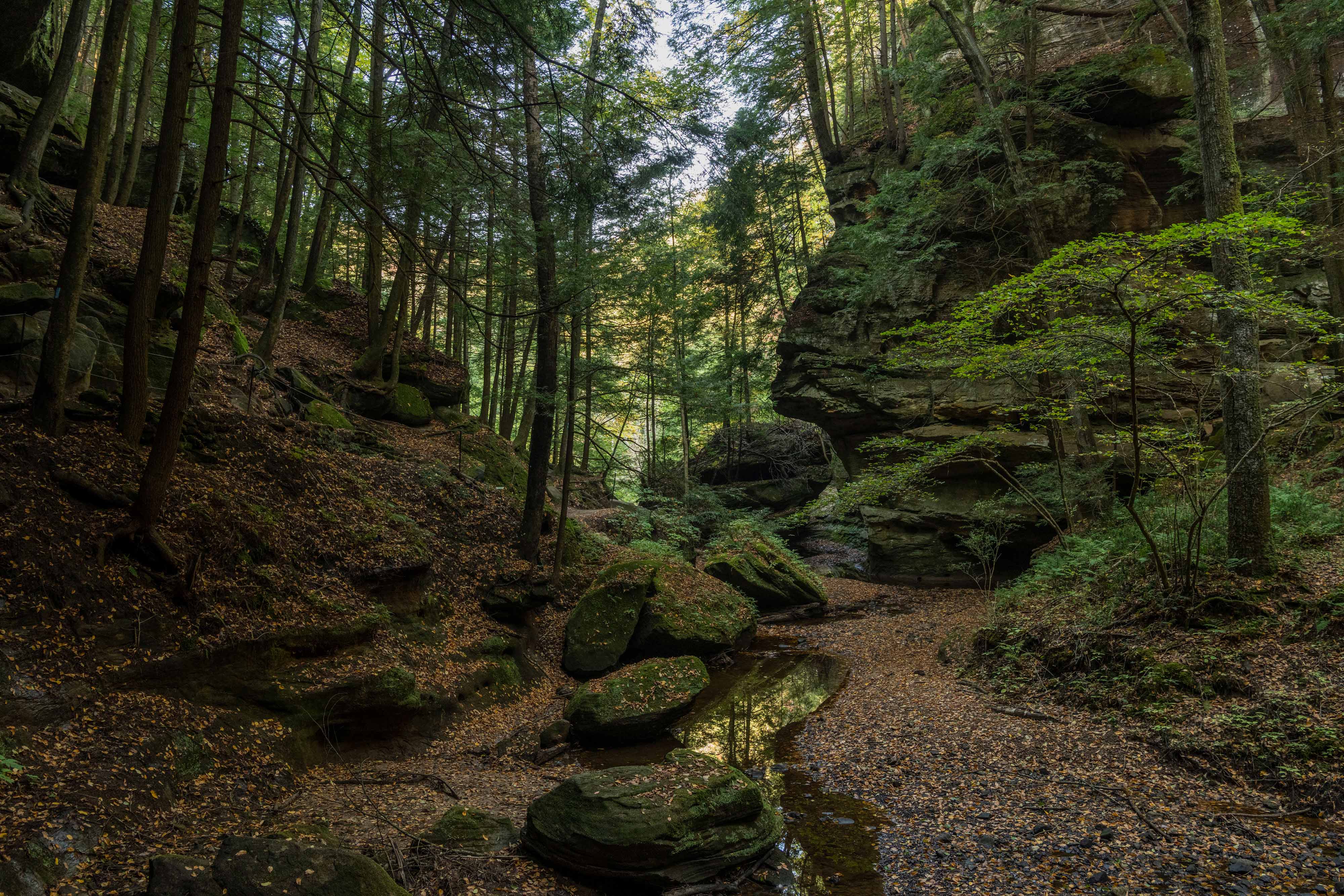
WEST VIRGINIA
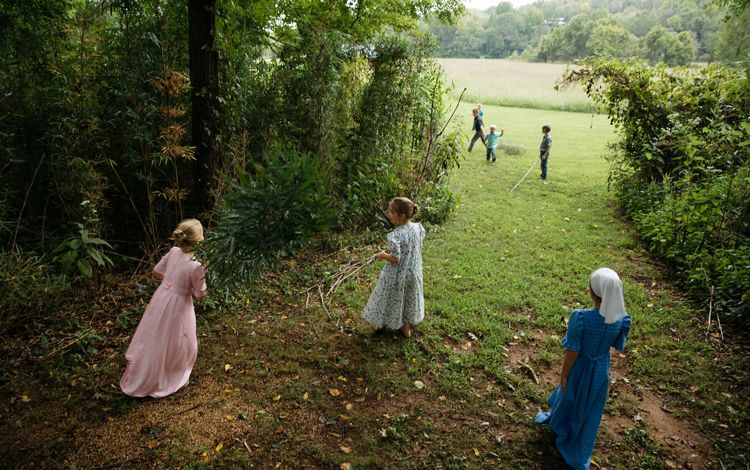
West Virginia contains some of the easternmost portions of the basin and includes the Monongahela and Ohio Rivers. The state is home to some of the most climate change resilient land in the U.S., from rolling hills to the Appalachian Mountains and plentiful freshwater throughout. There are numerous parks and preserves in the state including TNC’s Charlotte Ryde Preserve at Cheat Canyon, where the Cheat River (a whitewater-rafting destination and Ohio River tributary) can be found. For centuries, people have sought adventure, solace and creative inspiration in this wilderness and others like it. The COVID-19 pandemic has only increased that appreciation for this aspect of nature.
West Virginia also has a history of mining and mineral extraction in some parts of the state. As it transitions out of some of these industries, TNC in West Virginia is working with local community members to create both a healthy economy and a healthy environment. Find out more here.
West Virginia
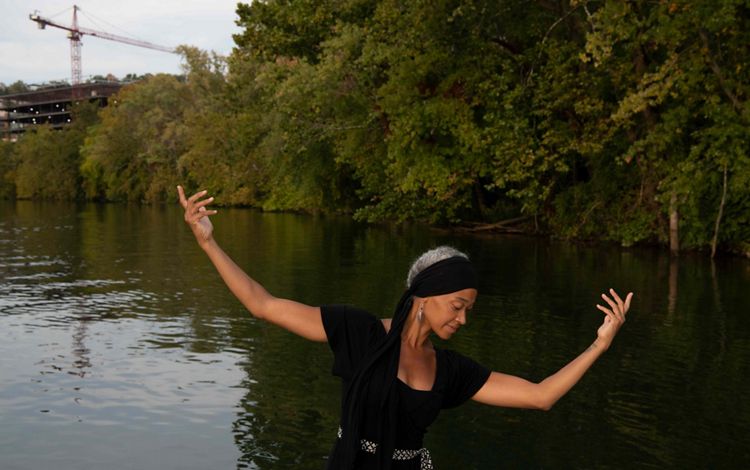
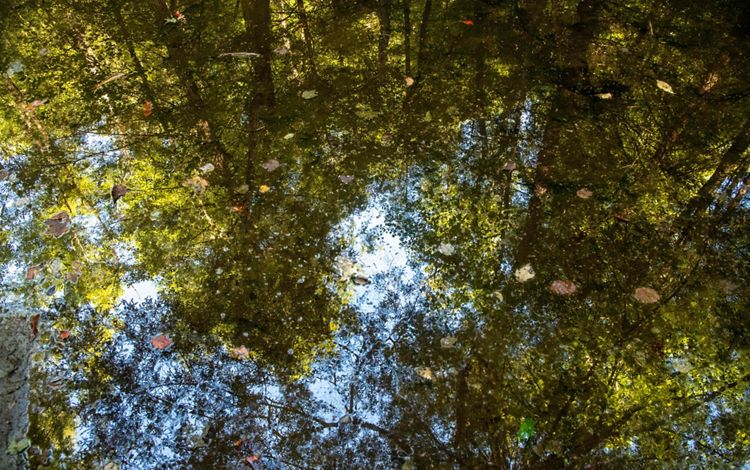
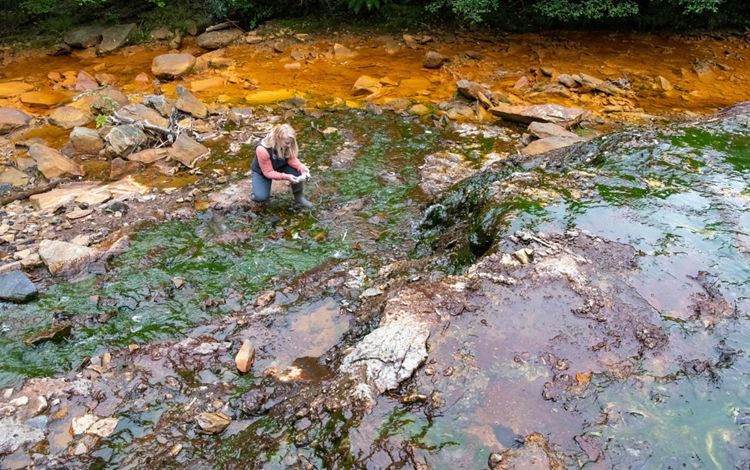



_________

Photographs by: Alex Snyder
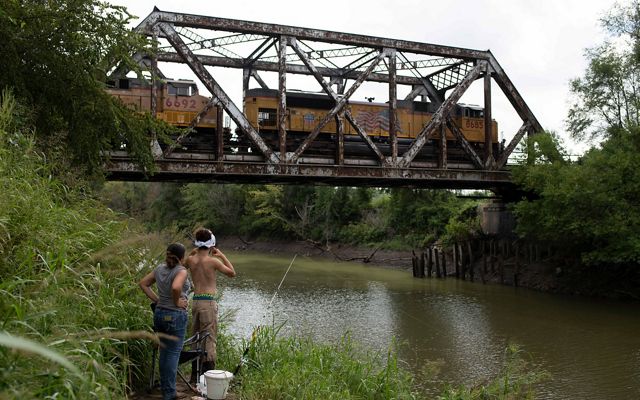
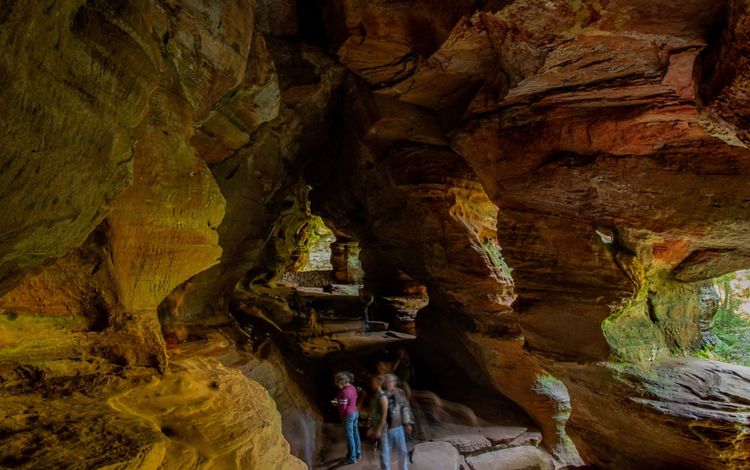
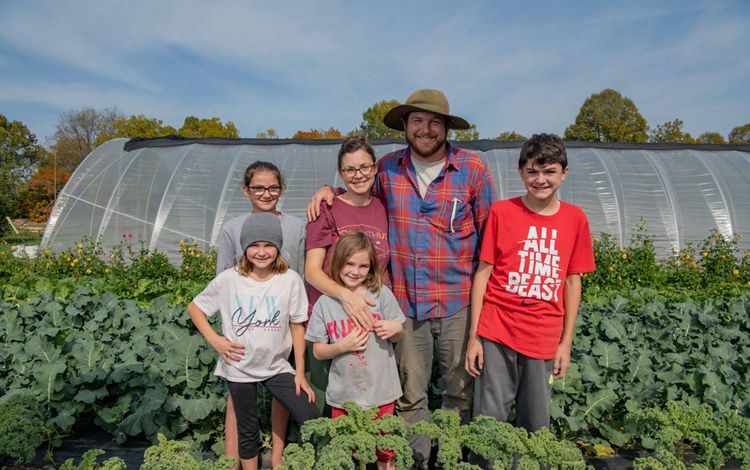
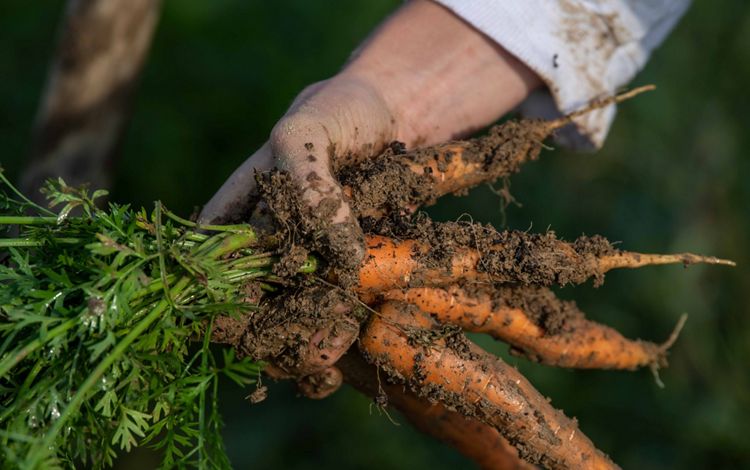
OHIO
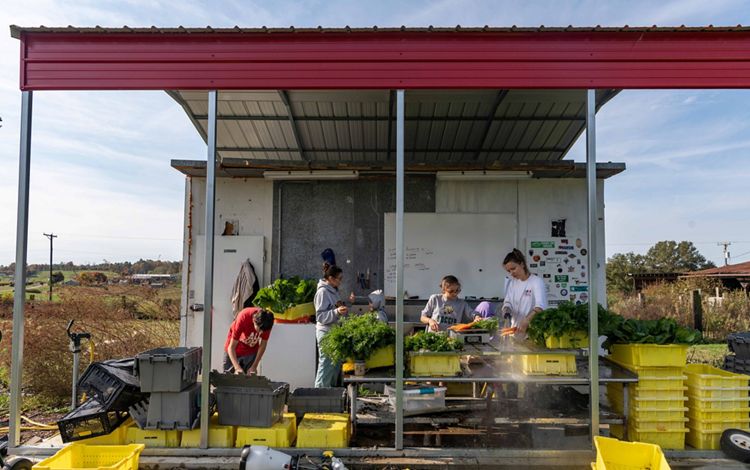
The Ohio River, a major tributary of the Mississippi River, creates the southern border of the state of Ohio. Here, the river passes through many rural communities before making its way to Cincinnati. In the southeastern part of the state, forested areas containing rock formations carved from glacial retreat attract nature lovers from around the region. Flat land, rich soil, and plentiful rainfall make for prime farmland as well. Large and small farms along creeks and streams that flow into the Ohio River rely on this water for their crops. To protect the Ohio River and its water quality, TNC is restoring streams and wetlands within the state and partnering with farmers to prevent nutrient runoff.
Ohio




_________

Photographs by: Dan Videtich
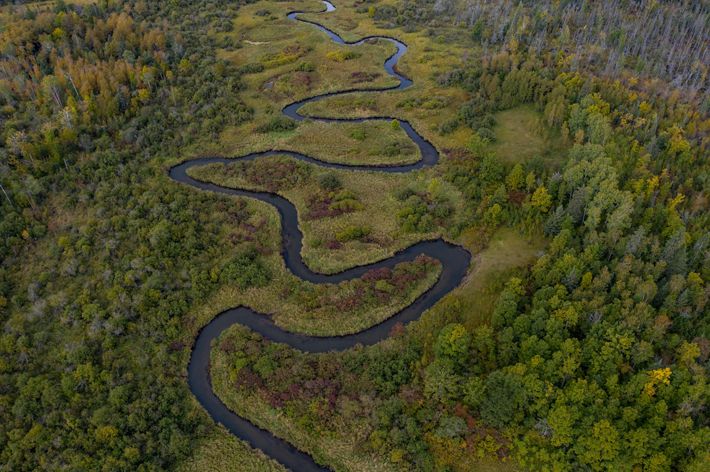
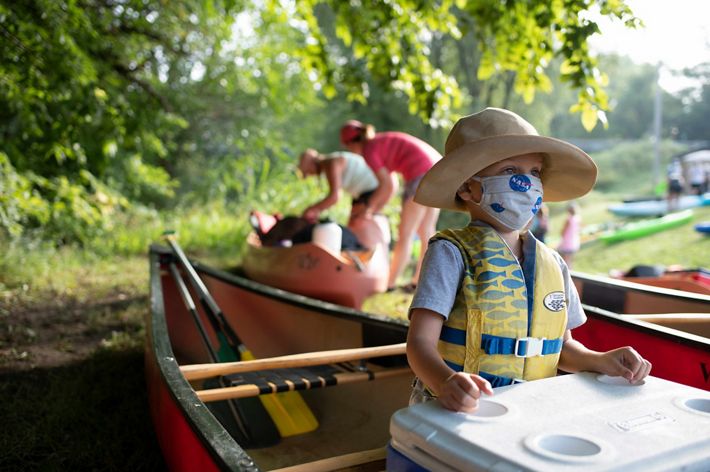
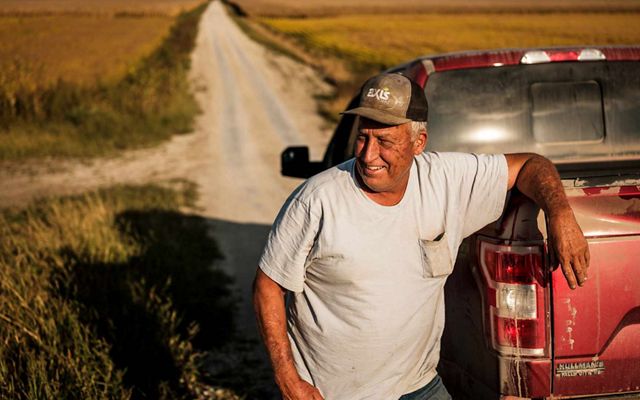
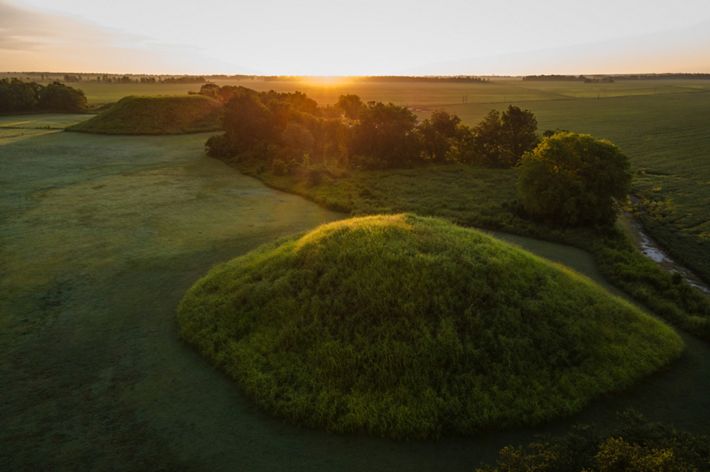
KANSAS
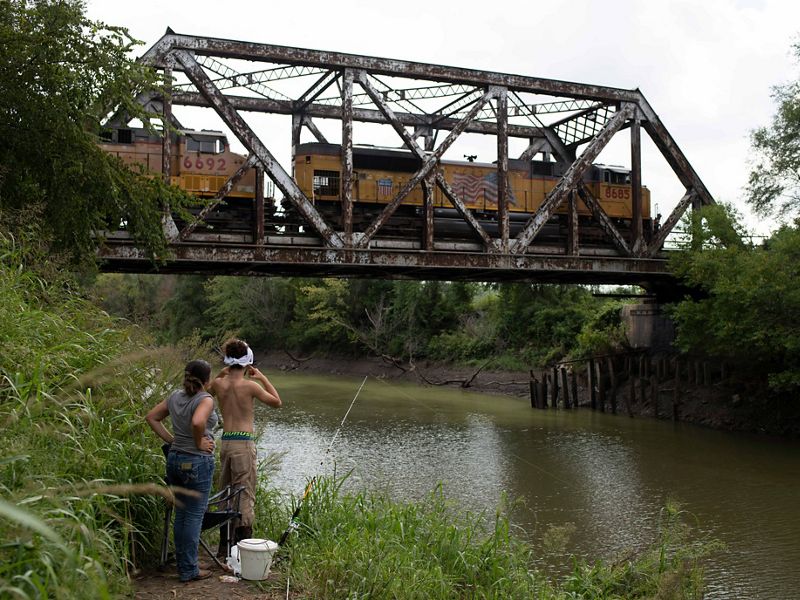
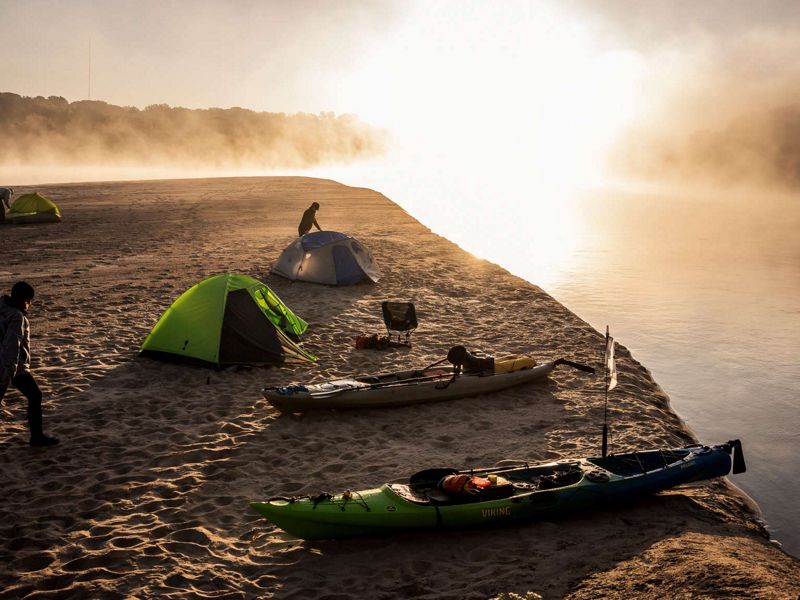
The Kansas River, known to locals as the “Kaw,” is one of the longest prairie rivers in the world. It is largely undammed which makes its free-flowing, shallow waters a great place for canoeing, fishing and kayaking. Because of its high silt content there are also many sandbars that make for great camping spots. However, that same high level of silt attracts river dredging on the Kaw—a practice that can negatively affect water table levels and cause land erosion. There are many organizations founded to help raise awareness of the health of the Kaw, and their efforts include getting locals out onto the water for cleanups and recreation, further deepening the community’s connection to the river.
TNC in Kansas helps to protect freshwater in the state through the David T. Beals III Healthy Streams for Kansas Initiative. Learn more here about their work on the Kansas River and other waterways.


_________

Photographs by: Dan Videtich
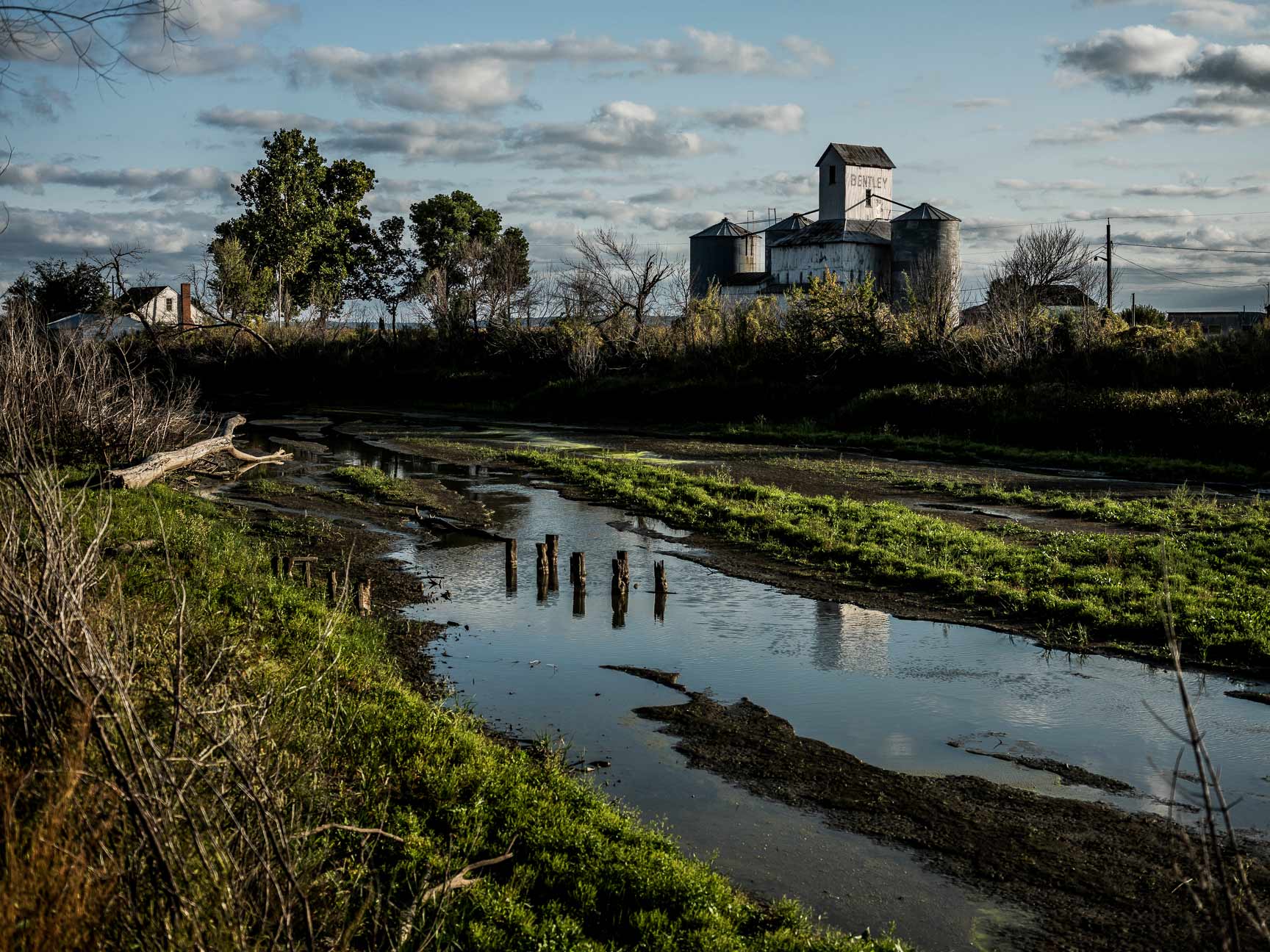
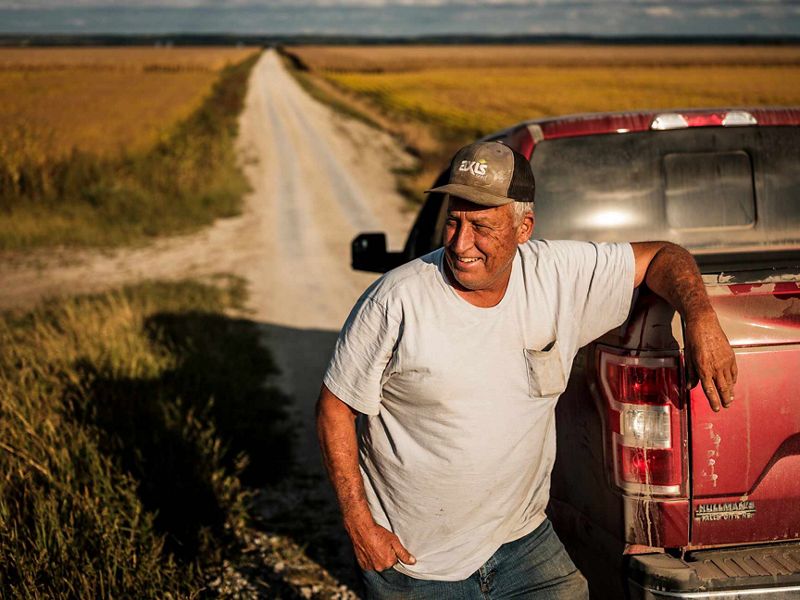
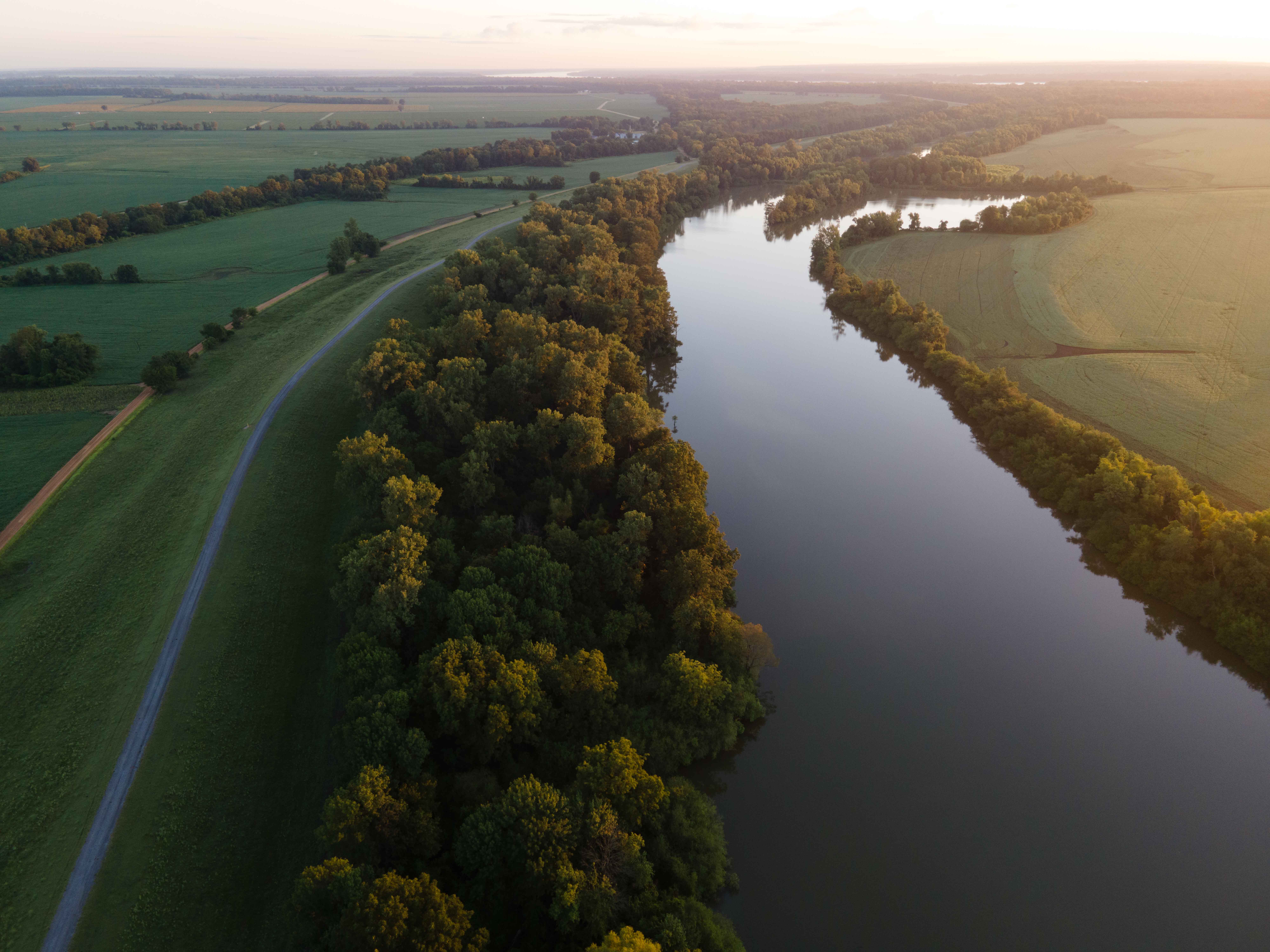
MISSOURI
“These flood waters are not receding,” read the testimony of Rhonda Wiley, Emergency Management Director for Atchison County, in a 2019 hearing regarding assessment of federal recovery efforts following recent disasters. For approximately 200 days that year, residents of Atchison and Holt County, Missouri, endured flooding as a result of levee failures. High water breached more than 100 levees in the Missouri River that year, and more than one million acres containing farms, railroads and highways were damaged. The Atchison County Levee District worked with landowners (with assistance from TNC) and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers to make the case to reconstruct one levee further back from the main stem of the river to better protect lands against extreme flooding in the future. Construction began in 2020, offering peace of mind to those who live along this 60-mile stretch that borders the Missouri River.
Read more about TNC's work on this project here.


_________

Photographs by: Terra Fondriest
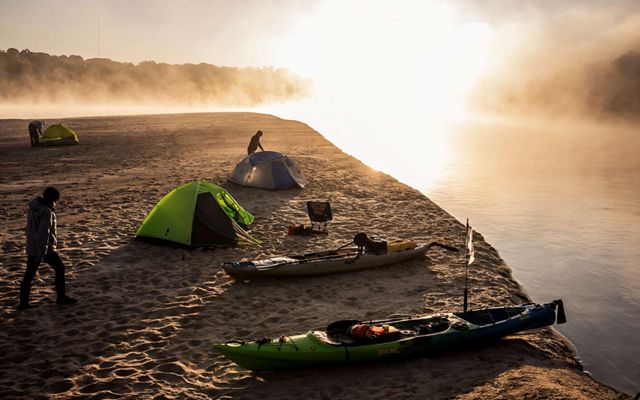
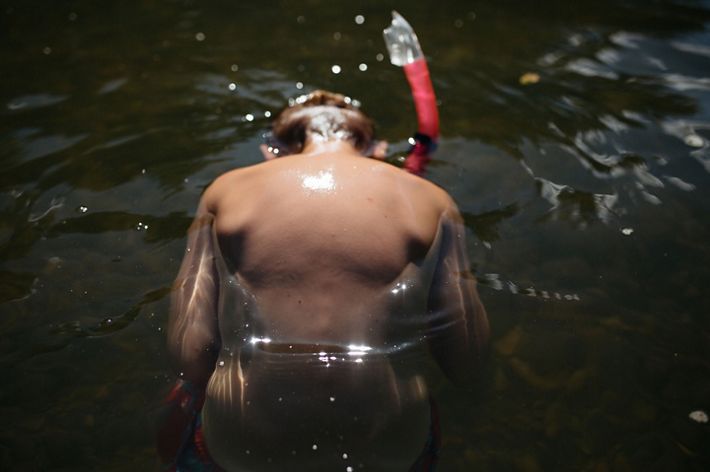
ARKANSAS
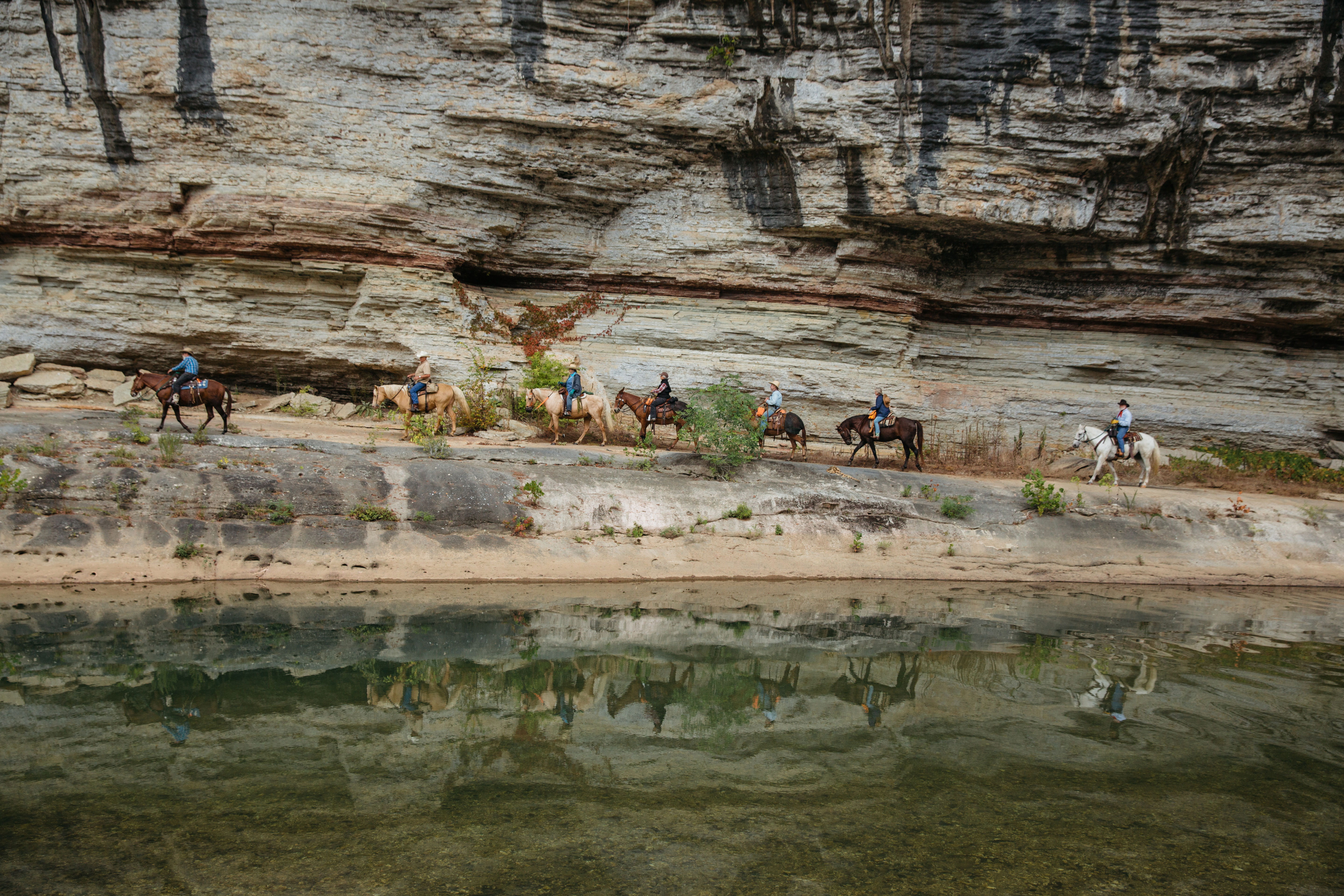
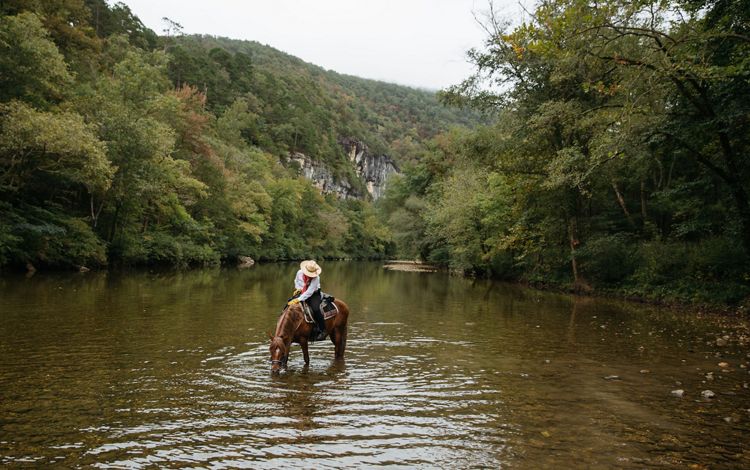
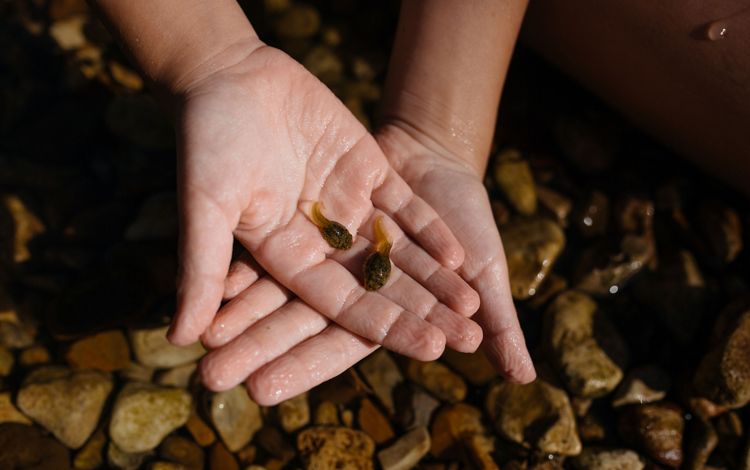
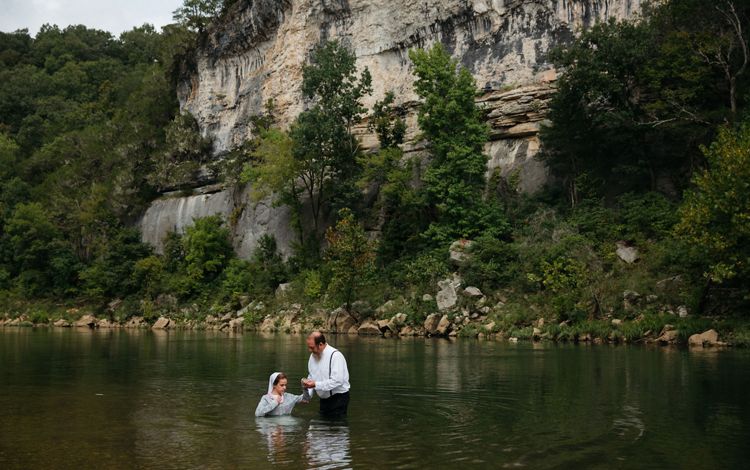
The Buffalo National River in northern Arkansas is a tributary of the White River and the first designated national river in the country. Natural beauty abounds in this area of The Ozarks, where waterfalls, limestone bluffs, caves and natural springs can be seen. The Buffalo River is home to hundreds of species of fish and other aquatic life and the surrounding land is home to the state’s only elk herd. The river attracts many types of visitors, be they on horseback or boat, and for recreational to religious purposes.
Find out how TNC in Arkansas helps to protect the Buffalo National River here.
Arkansas




_________

Photographs by: Rory Doyle
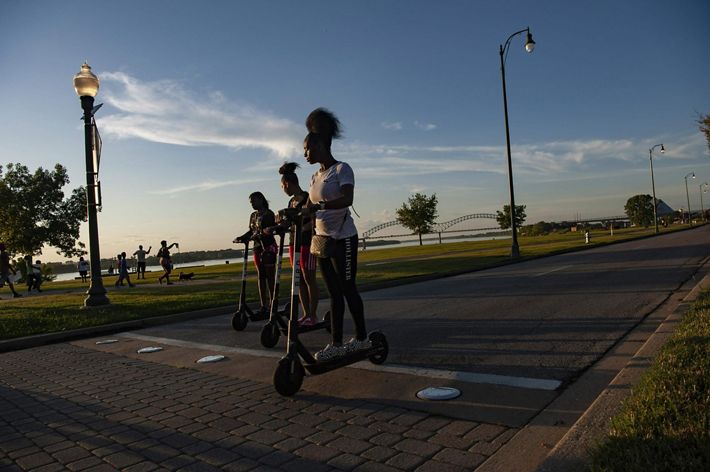
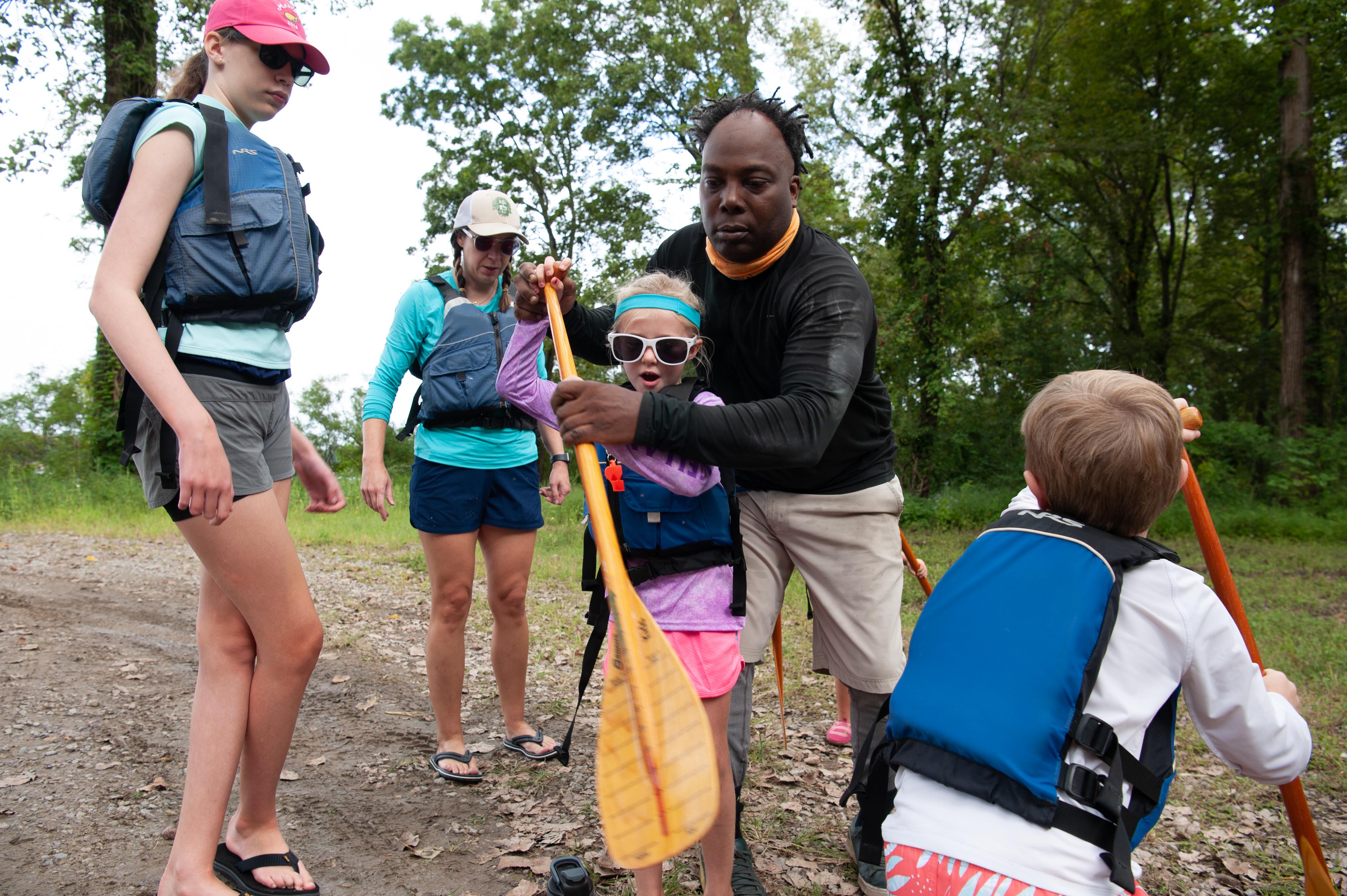
TENNESSEE
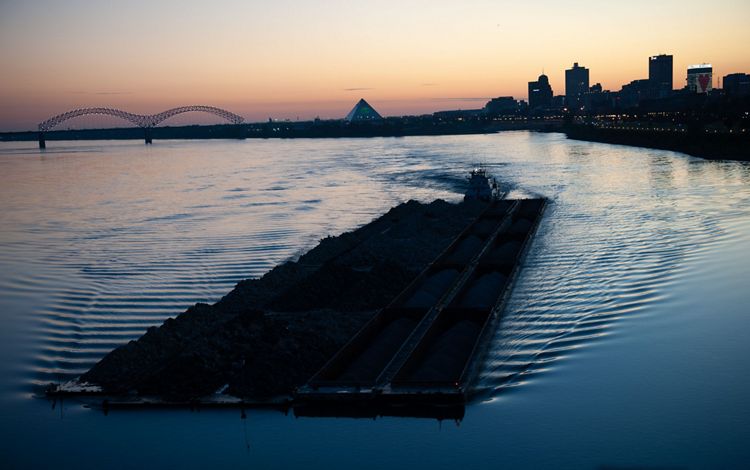
Cities dot the water's edge throughout the Mississippi River basin. They developed there often for industrial purposes or proximity to water-based transportation. Founded in 1819, Memphis sits at a relatively high location above the river, making it less prone to floods and a desirable place to live. It became a major trade and transportation center. Today, the International Port of Memphis is the fifth largest inland port in the country. Meanwhile, the city has been able to take advantage of its waterfront property, where residents can enjoy the green space and pedestrian paths at the newly constructed Tom Lee Park.
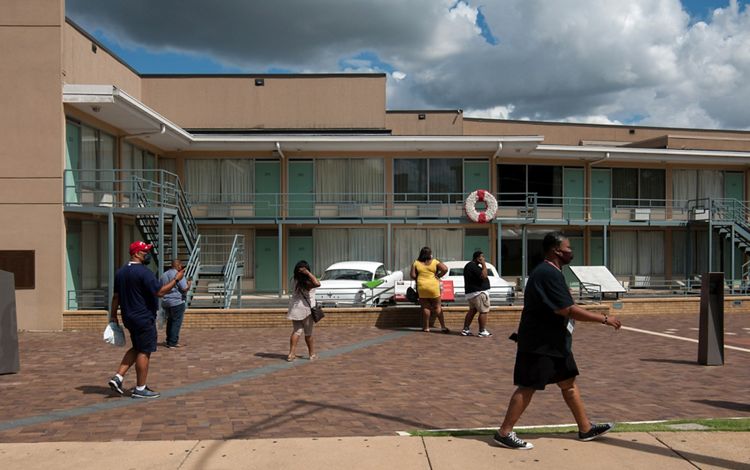
Its central location and access also made Memphis a cultural hub in the 20th century. Blues musicians throughout the Mississippi Delta gathered there and exported their sound to cities and towns throughout America. During the Civil Rights Movement, Memphis was a central spot for many events within the movement, including the 1968 Memphis Sanitation Workers’ strike and the tragic assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.. The city created the National Civil Rights Museum at the Lorraine Motel, the site of the assassination, to honor the work that continues to this day.
The Nature Conservancy in Tennessee works throughout the state on freshwater initiatives, including efforts to preserve the biodiversity of the Tennessee River, the largest tributary of the Ohio River and part of the Mississippi River basin. Find out more info here.
Tennessee





_________

Photographs by: Rory Doyle
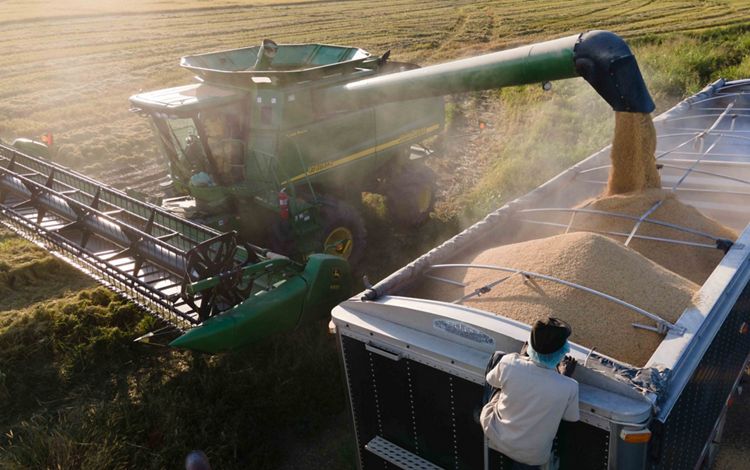
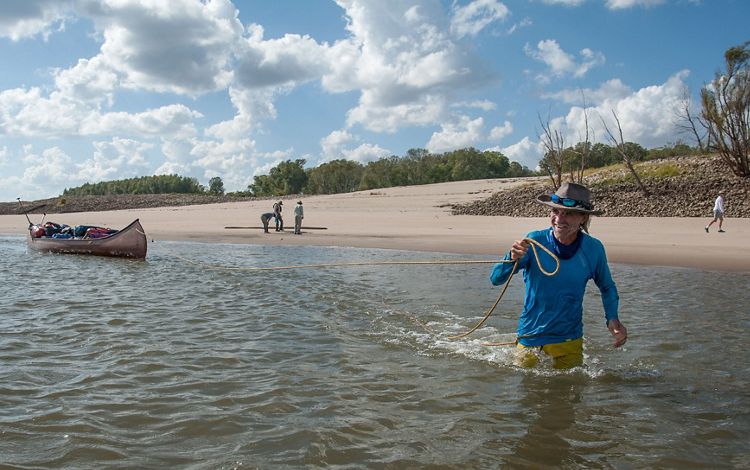
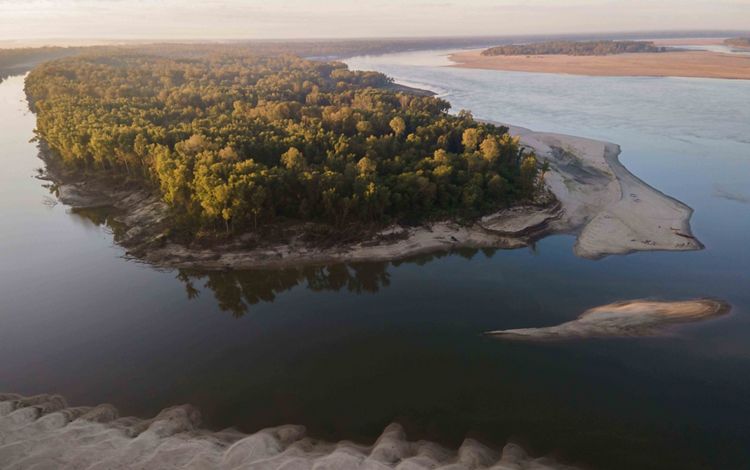
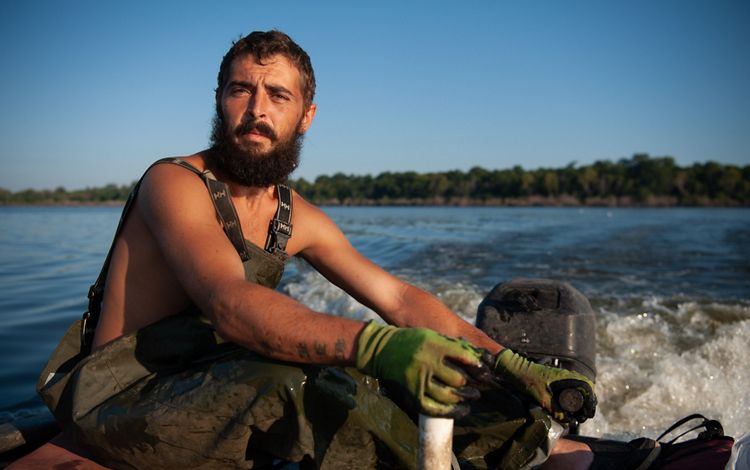
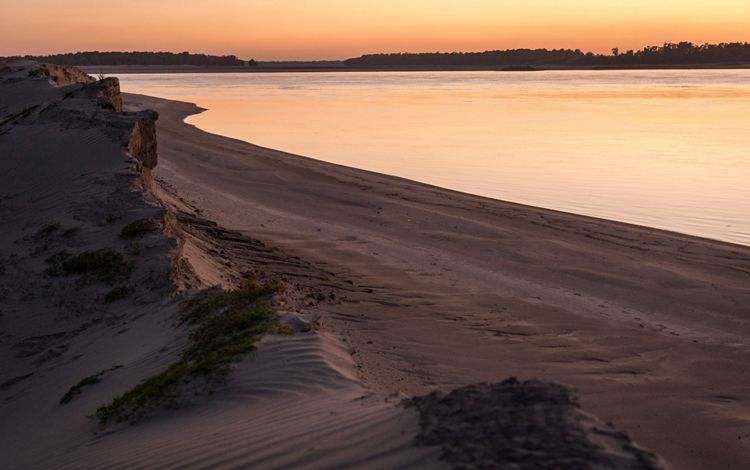
MISSISSIPPI
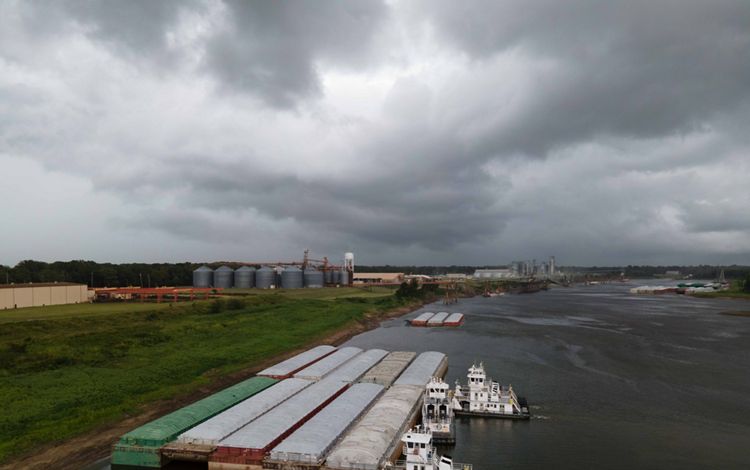
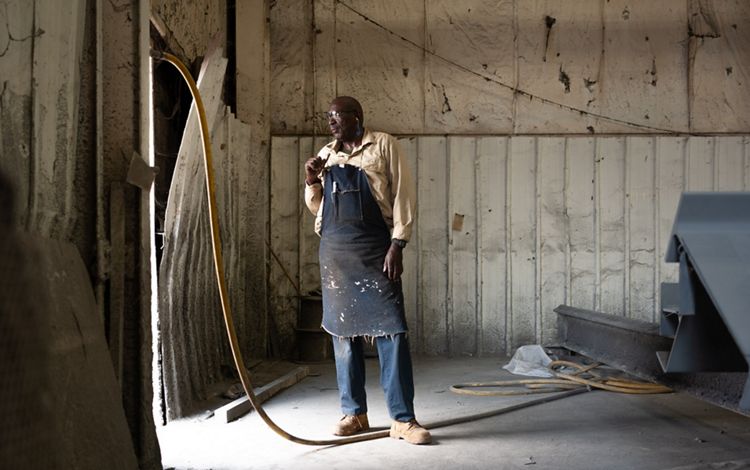
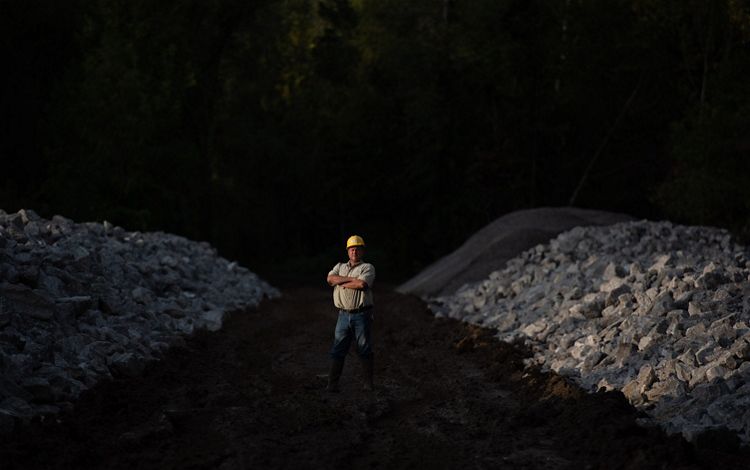
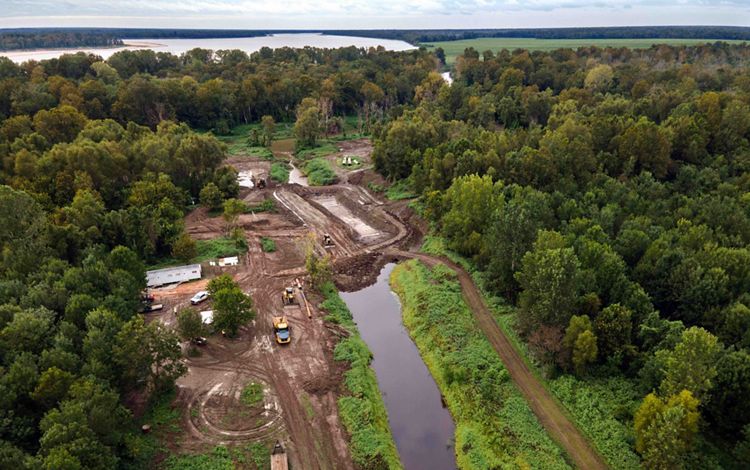
By the time the Mississippi River reaches the state of Mississippi, it has become a meandering and changeable force. This portion of the river is scattered with oxbow lakes, which serve as ghosts of the water’s change of course. It is also carrying with it much of the 500 million tons of sediment that eventually spills downriver into the Gulf each year and gives the Lower Mississippi its muddy hue. Much of this region’s bottomland hardwood forests have been removed to create room for agriculture, and the river is heavily used for commercial transport. But, there is also wild beauty to be found in this part of the river and individuals who are making it their life’s mission to restore local residents’ connections to the beauty of the Mississippi. While engineering and nature-based solutions have helped to control this river, humans have always respected the might and whims of its borders.
For more information about the work throughout the Mississippi River basin, click here.
Mississippi










_________

Photographs by: Rory Doyle
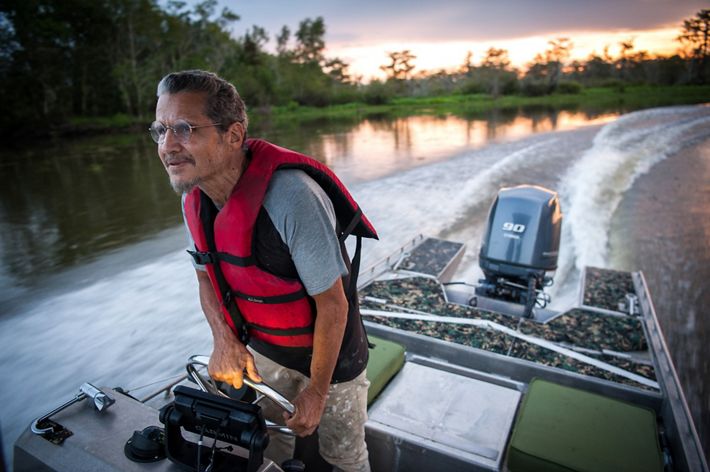
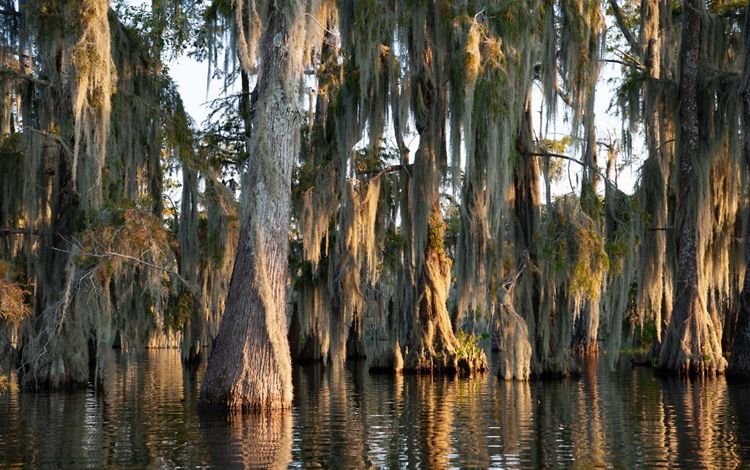
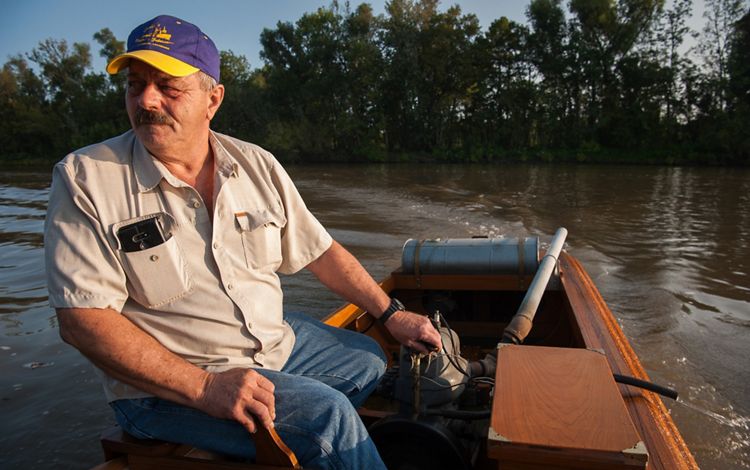
LOUISIANA: THE ATCHAFALAYA
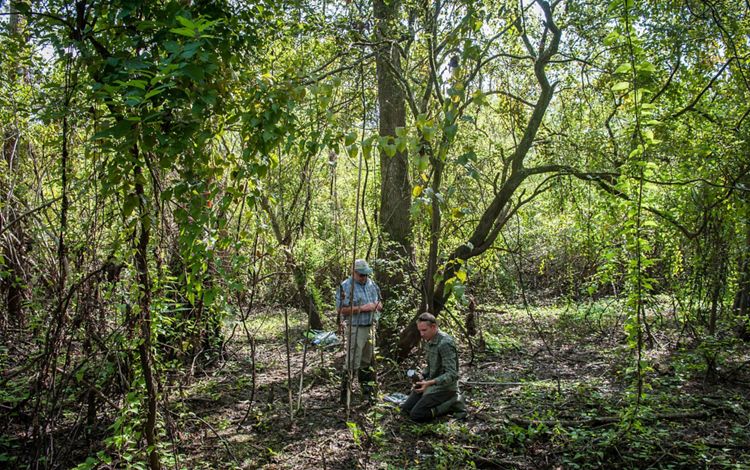
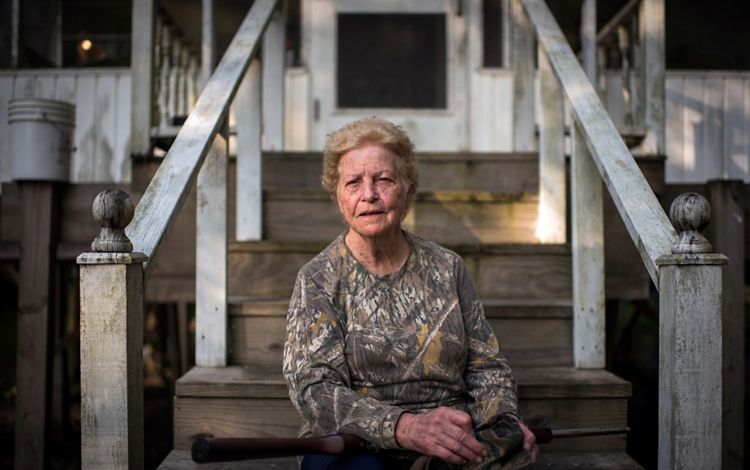
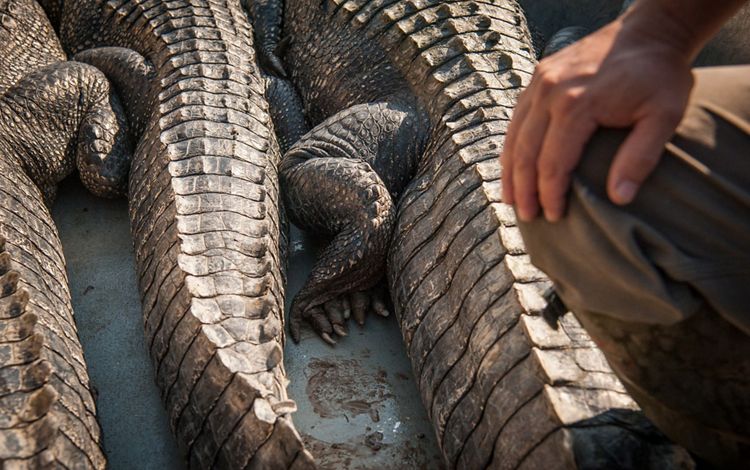
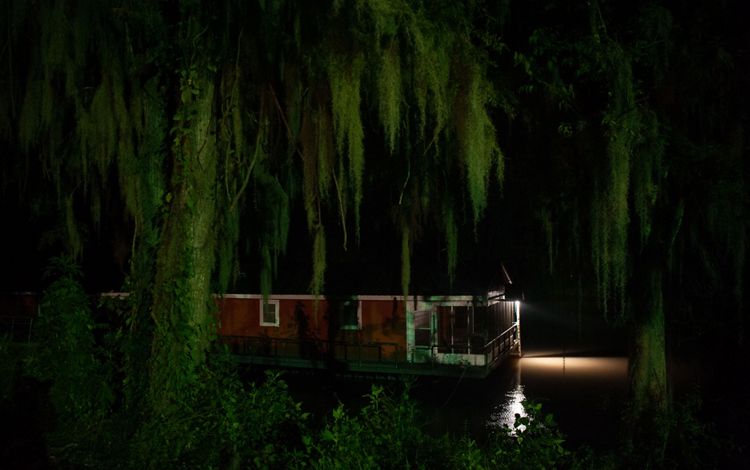
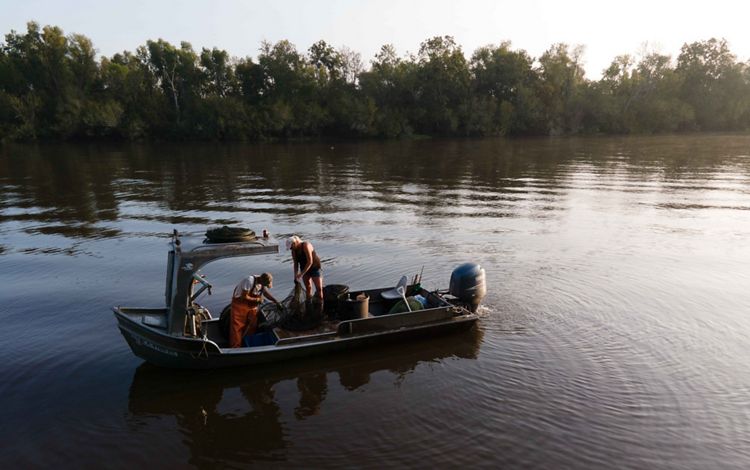
The Atchafalaya River basin is home to a blend of cultures and people, all of whom had to adjust to their swampy surroundings upon arrival in a place where boats are a travel necessity. The terrain shaped residents' lives and generated bits of culture unique to the region. Creole and Cajun language, music and food all have roots in the Atchafalaya. The Atchafalaya River is a western distributary for the Mississippi River, and the water that flows within it eventually spills downriver into the Gulf. Throughout the Atchafalaya, low-lying swamps, forests and wetlands abound. The Chitimacha tribe, who still reside in the basin today, were some of the earliest hunters, fishers, loggers and farmers in this region. Many modern-day residents still use the natural resources of the basin for sustenance and for income, and tourists now visit the Atchafalaya for its natural beauty and recreational opportunities such as bird-watching and boating.
To find out about how TNC is working with the community in this region, click here.
Louisiana: Atchafalaya River Basin







_________

Photographs by: Akasha Rabut
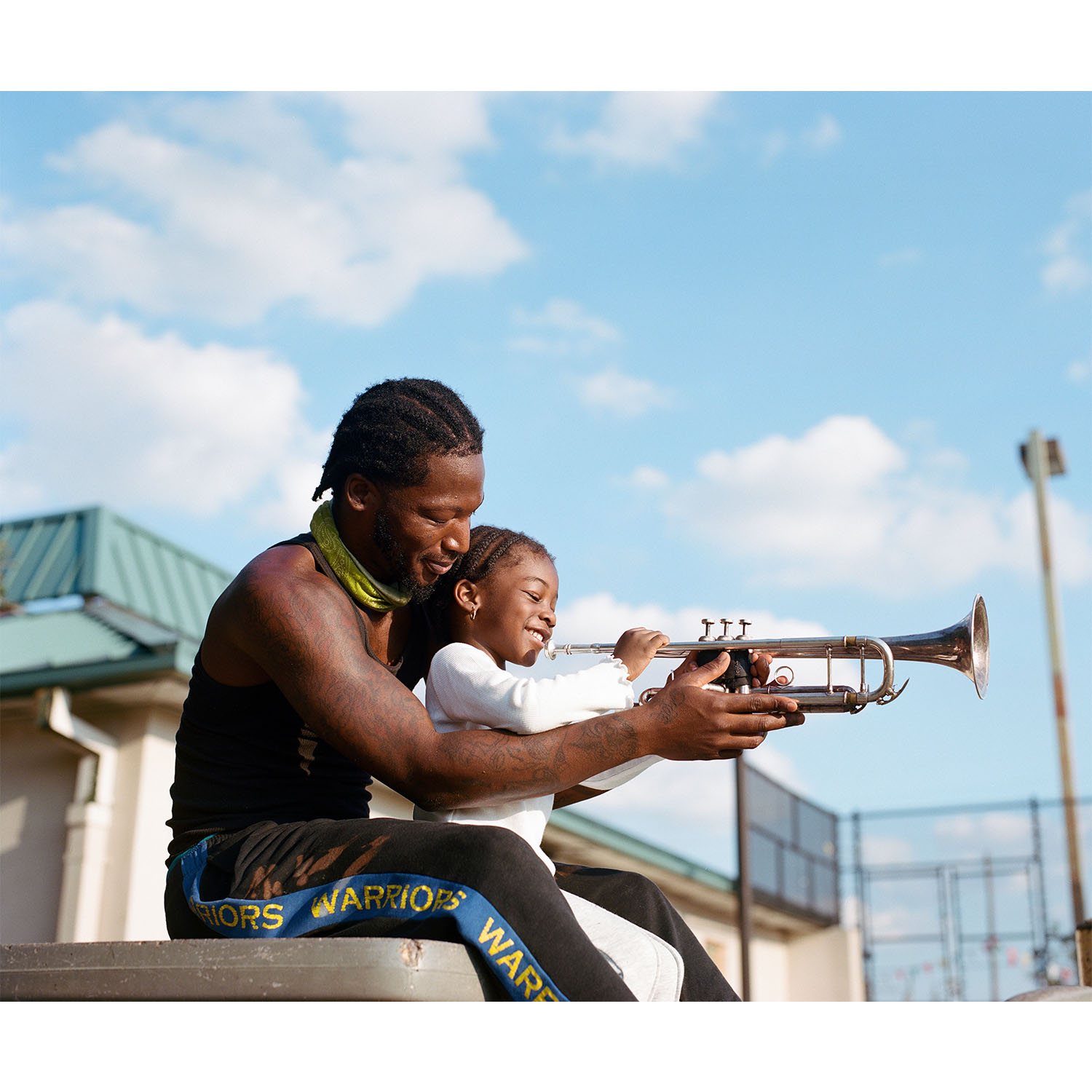
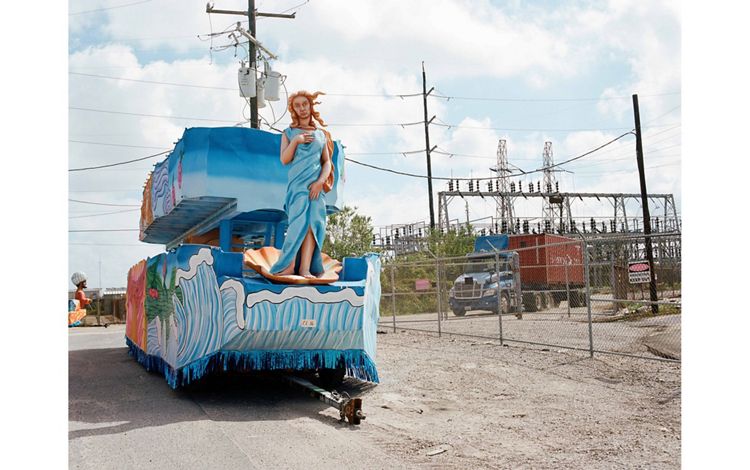
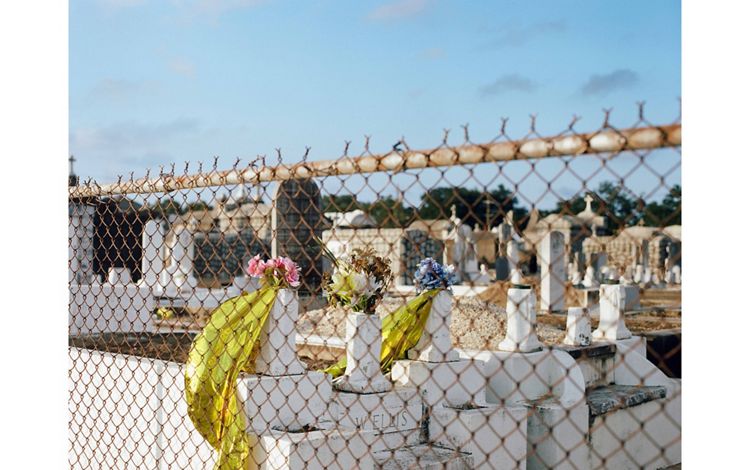
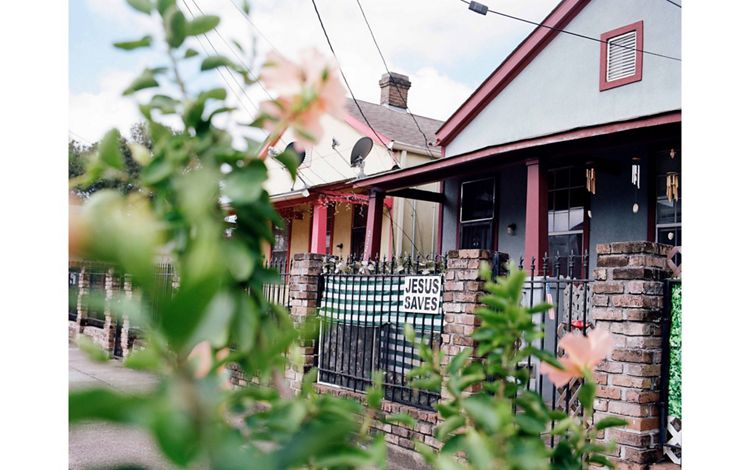
LOUISIANA: NEW ORLEANS
New Orleans is the last urban stop for the Mississippi River before it spills into the Gulf. The equivalent of 166 semi-trailers worth of water flows past the Big Easy each second. Tucked alongside the Mississippi and surrounded by lakes and wetlands that fade into the Gulf of America, half the city lies below sea level and is sinking at roughly one centimeter per year. About one football field’s worth of coastal Louisiana’s wetlands, which help to absorb some of a storm's impact before it reaches the city, is lost every one and a half hours, making New Orleans’ very existence an unlikely phenomenon. In spite of—or perhaps because of—the fragile existence of the city, its residents have created a culture that seems to embrace every moment and the beauty within it. From the music and dance of the Second Line tradition to Mardi Gras celebrations, a rich history of “letting the good times roll” is the beating heart of New Orleans. But as storms increase and land becomes more precious, cascading side effects from climate change arise, including gentrification in places like the Central City neighborhood.
TNC is working throughout the Gulf Coast to fortify shorelines via natural climate solutions. Find out how this work is being done here.
Louisiana: New Orleans

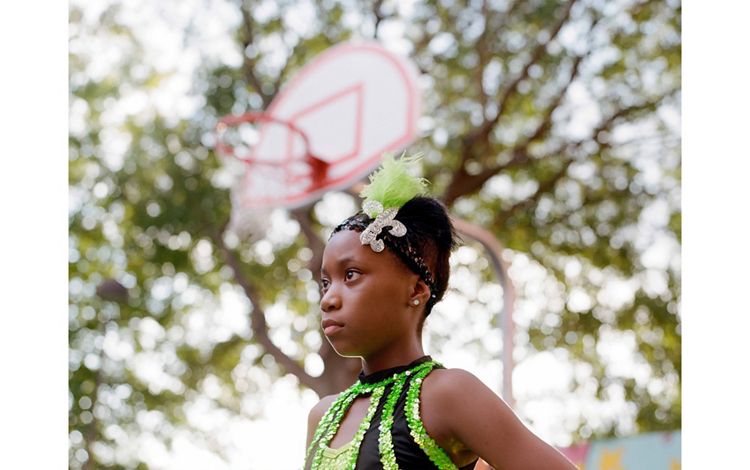





Get the Magazine
Sign up to become a member of The Nature Conservancy and you'll receive the quarterly print edition of the magazine as part of your membership.

















